 Radiocarbon dating of carefully extracted fatty-acid compounds could become a robust archaeological tool. Read more in Physics Today…
Radiocarbon dating of carefully extracted fatty-acid compounds could become a robust archaeological tool. Read more in Physics Today…
Outlets
- APS Physics (232)
- Berkeley Lab (35)
- Cleantech Concepts (5)
- Encyclopedia of Puget Sound (1)
- Eos (1)
- Europa Science (14)
- IEEE Spectrum (12)
- MRS Bulletin (19)
- Nature (1)
- New Scientist (1)
- Old News (7)
- Pacific Northwest National Lab (8)
- Physics Today (154)
- Physics World (2)
- Science Magazine (15)
- Science News (4)
- Scientific American (30)
- SPIE News (4)
- SPIE Professional (3)
- Tech & Content Writing (5)
- The Scientist (4)
- Travel Writing (4)
- Uncategorized (7)
Topics
- Acoustics
- APS Physics
- Astronomy
- Astrophysics
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Atomic and Molecular Physics
- Batteries
- Berkeley Lab
- Biochemistry
- biology
- Biophysics
- Chemistry
- Climate Change
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Conferences
- Down to Earth
- Earth Sciences
- Ecology
- Electronics
- Energy
- Environment
- Europa Science
- Fluid Dynamics
- Geology
- Geophysics
- IEEE Spectrum
- Lasers
- Magnetism
- Materials Sciences
- Medical
- Metamaterials
- Meteorology
- MRS Bulletin
- Nanoscience
- Nuclear Physics
- Oceanography
- Optics
- Photonics
- Physics
- Physics Today
- Plasma physics
- Policy
- Quantum Mechanics
- Quantum Physics
- Scientific American
- Seismology
- Semiconductors
- Soft matter
- Spectroscopy
- Volcanology


 A consortium of high-performance computing centers helps fast-track COVID-19 vaccine, drug, and epidemiology calculations.
A consortium of high-performance computing centers helps fast-track COVID-19 vaccine, drug, and epidemiology calculations. 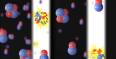 The loss of ultracold molecules from an optical trap comes from optical excitation of the complexes that form when two of the molecules collide.
The loss of ultracold molecules from an optical trap comes from optical excitation of the complexes that form when two of the molecules collide.  Unified theory describes formation of huge, mysterious waves.
Unified theory describes formation of huge, mysterious waves. 
 Stable compounds made from helium and ammonia are predicted to form at the extreme pressures found inside Neptune and Uranus.
Stable compounds made from helium and ammonia are predicted to form at the extreme pressures found inside Neptune and Uranus. 
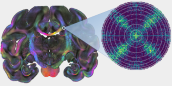 Light-scattering measurements and high-performance computing enable mapping of complex nerve fiber organizations in the brain.
Light-scattering measurements and high-performance computing enable mapping of complex nerve fiber organizations in the brain.  Volcanologist Alexa Van Eaton explains the origins of electrical activity in volcanic ash plumes and why it sometimes leads to detectable lightning.
Volcanologist Alexa Van Eaton explains the origins of electrical activity in volcanic ash plumes and why it sometimes leads to detectable lightning.